
Many of the terms that are used to talk about reproduction are confused and even unknown to many people. Generally, the word fetus is used to refer to the baby growing in the wombHowever, the gestation period goes through a series of phases from when fertilization occurs.
The three terms, zygote, embryo and fetus, are used in reproductive biology to refer to the future baby. But each of these names refers to the different stadiums the little one goes through throughout the gestation period. Knowing the difference between all these terms will be very useful whether you are pregnant or if you are planning pregnancy.
On many occasions when newly pregnant women arrive at the doctor's office, they begin to hear medical terms and words that are totally unfamiliar. Much more so when future parents undergo a process of Assisted reproduction. Therefore, having basic knowledge about reproduction can help you better understand the process that will lead you to become a mother or father.
The zygote
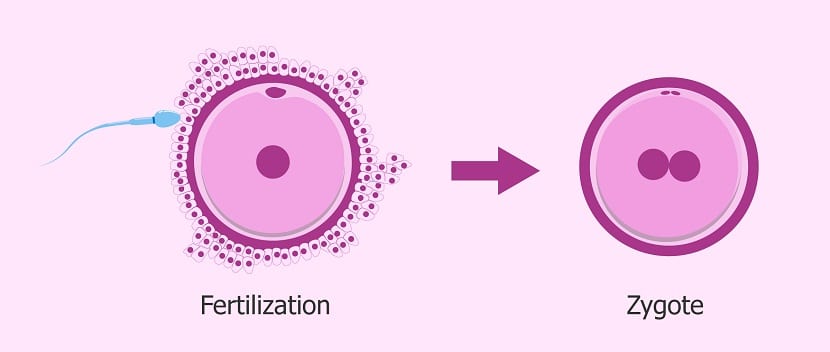
When the female gamete (the ovum) and the male gamete (the sperm) unite, the phenomenon of fertilization occurs, which results in a new cell. This new cell contains genetic material in equal parts of the mother and father, so it contains 23 chromosomes from the father and 23 from the mother. Therefore, the zygote is the result of the fertilization of the ovum by the sperm.
The zygote is the first stage of life and since its constitution it is loaded with DNA with genetic information on future aspects such as physical, for example. However, despite being one of the most important stages of reproduction, since it is the beginning of life, the new being is called zygote for a very short time, approximately 24 hours nothing more. Once those first hours pass, the zygote is segmented into cells and thus begins the next period, the embryonic one.
The embryo

With cell segmentation, the second period of gestation begins, which is known as the embryonic period. This second stage of life lasts approximately 8 weeks in the case of humans and during this time, the new being will acquire characteristics of each species.
From day 1 after the zygote stage, embryonic development and cell division begin. As the cells increase, the different organs and tissues of the future baby will be created. During the next 8 weeks, the embryo will undergo important changes produced by cell division. Even the embryo itself can acquire a different name during those first weeks.
- Morula: In this phase the embryo is made up of a large group of identical cells. These they are grouped forming a kind of blackberry, and hence the term morula originates. This happens around the fourth day of embryonic development.
- Blastocyst: Cells begin to differentiate, giving rise to two groups of cells. This occurs between the 5th and 6th day of embryonic development. From this moment on, the placenta and all the structures necessary for the pregnancy to develop normally will begin to form.
Fetus
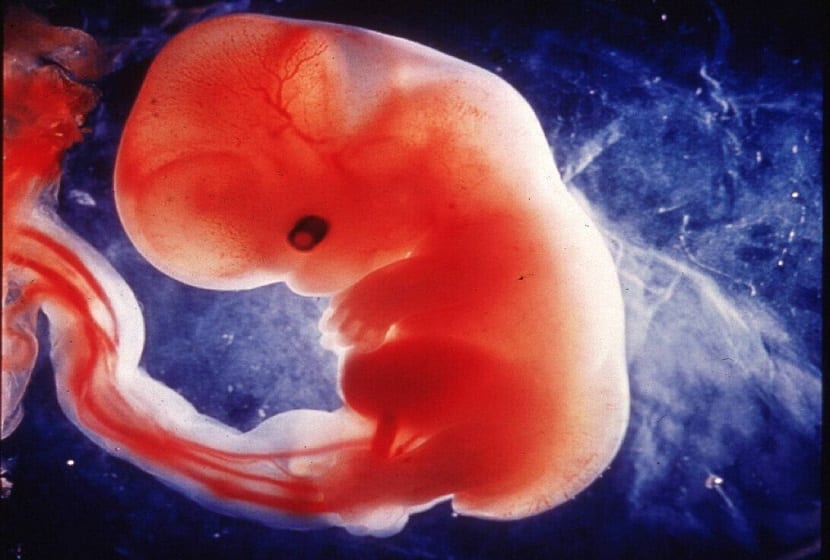
When the embryonic stage is completed, the new being has organs and as the limbs develop, this period ends, giving rise to the longest of gestation, the fetal stage. From this moment, cells begin to specialize. For the next several months until the baby is born, they will go away forming and developing all tissues and organs.
Organs such as the brain, kidneys or liver begin to function during the fetal period. In addition, the fetus will acquire the physical characteristics of the baby that he will become. During all these weeks, the little one will grow and develop fully, as long as the pregnancy proceeds normally. In the prenatal check-ups you will be able to listen to your heartbeat, see how your future baby moves or even blinks.
And so it's like the magical process of life begins.