
In this review of the types of learning that can occur in the classroom, but also outside of it today we will talk about problem-based learning (PBL). This type of learning is a teaching method in which the student is the protagonist. It will be the boy or the girl who carries out the inquiry process that resolves the questions, doubts and uncertainties about complex phenomena in life.
In this method, knowledge has the same importance as the acquisition of skills and attitudes. It is a methodology, not an instructional strategy.
Description of problem-based learning
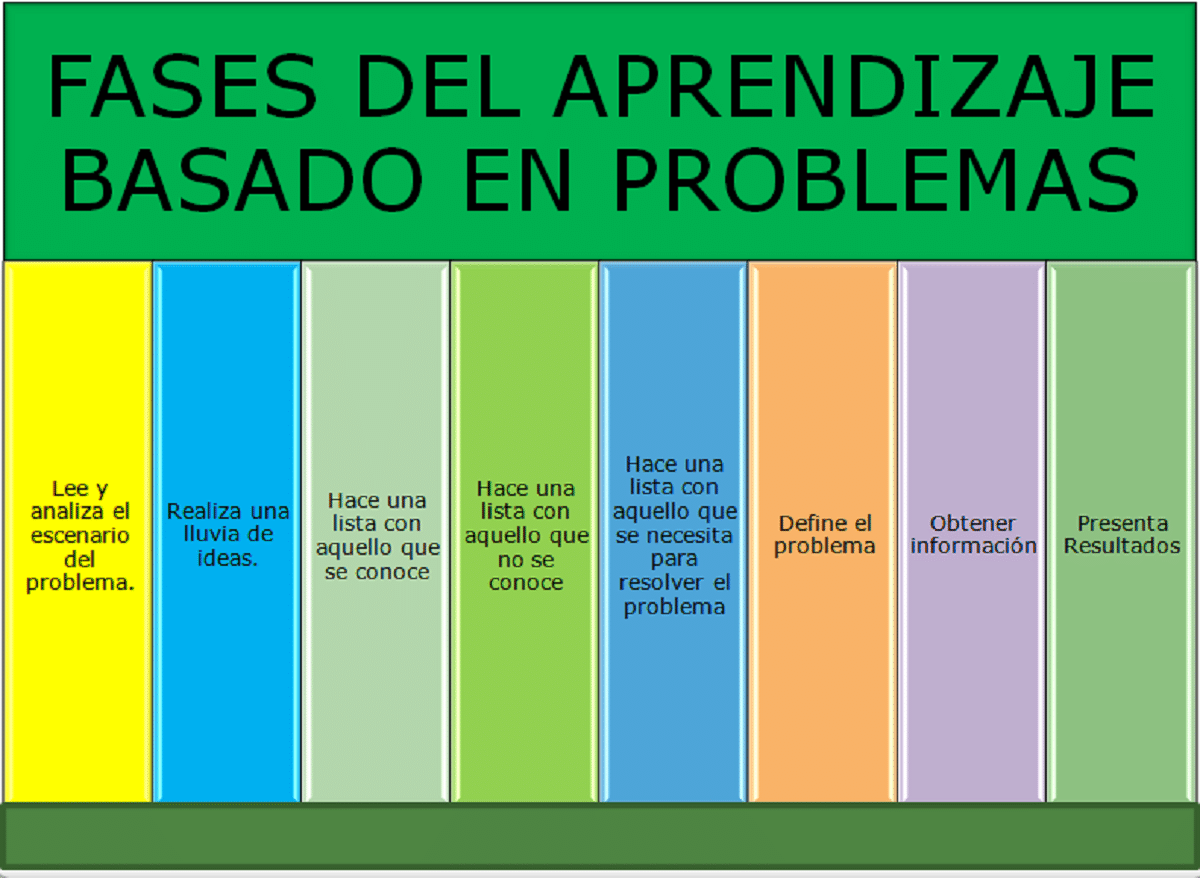
With this method the student is responsible for their own learning, and the teacher is only a guide. As has been said, problem-based learning is aimed at the search, understanding, assimilation and application of knowledge to solve a problem or answer a question.
When the study of any subject begins the child does not have enough knowledge and skills that allow you to solve the problem effectively. It is recommended that at this time each child individually make a list of what they know about the subject. This implies that students draw on what knowledge they already have, share their knowledge and the details of the problem. All this information is what they can use for later resolution.
At this stage, the student needs to know what you need to move forward in resolving the issue proposed, as the child progresses, he will be competent to plan and carry out interventions that will allow him to finally solve the problem adequately. The construction of knowledge will have been achieved, working cooperatively.
Problem-based learning facilitates interdisciplinarity and the integration of knowledge, crossing the barriers of fragmented knowledge itself in different disciplines and subjects.
Problem-based learning and constructivism

Problem-based learning is based on different theoretical currents, in particular in the constructivism. For this follow three basic principles:
- The understanding regarding a reality situation arises from the interactions with the environment. Students should be active, independent, and problem-oriented rather than passive receivers of information.
- El cognitive conflict By facing each situation, it stimulates learning. The teachers, who act as guides, seek to motivate and improve the initiative of the students. They are capable of learning on their own.
- Knowledge is developed through recognition and acceptance of social processes. Different individual interpretations of the same phenomenon are evaluated. Students work in teams to solve problems. They actively participate in solving the problem, they are the ones who detect their learning needs, investigate, learn, apply and solve problems.
Problem-based learning includes the development of critical thinking in the teaching and learning process. It is not something additional, it is a constitutive part of such process.
Emphasize the development of attitudes and skills

With problem-based learning different attitudes and skills are developed and emphasized that leads them to the active acquisition of knowledge and not only to the memorization of content. Students are divided into small groups of six to eight students who work collaboratively to solve common problems from the analysis.
Students develop critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and collaboration. While problems are identified hypotheses are formulated, who conduct the search for information, conduct experiments, and determine the best way to reach the solution. Students enjoy learning by stimulating their creativity.
They also acquire the responsibility in solving problems that are part of reality. The group ranks learning topics based on the diagnosis of their own needs, which in turn generates new learning needs. These needs are not imposed by a curriculum development, or the teaching staff, but are born from the approach of a problem to be solved.