A few days ago, a 2-year-old baby was admitted to the pediatric ICU of a maternal and child hospital in Extremadura, due to a possible severe meningitis; The Health Authorities quickly took the necessary prophylactic measures with the family, and of course, the child was cared for carefully and closely. Meningitis is a disease we know little about, and about which we have many doubts, so we will try to solve them with this post.
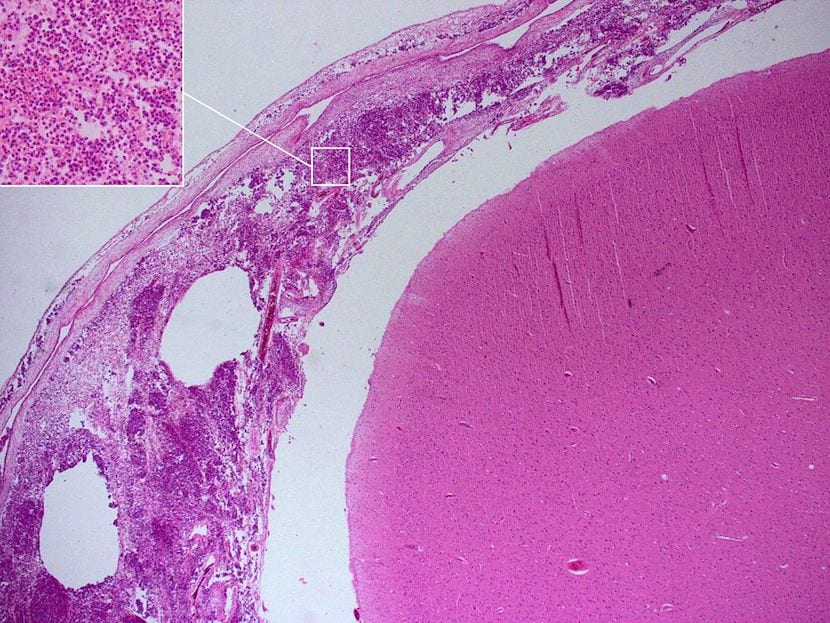
It is a serious viral or bacterial infection localized to the meninges (membranes that surround the spinal cord and brain). It can cause very extreme effects such as brain damage or seizures; or others including headache or fever. There are cases so serious that they end with the death of the patient. When we are informed of an episode of meningitis in our environment, alarms go off, since contagion between people who are close to the infected is relatively easy, by being transmitted through secretions of the respiratory system. But the response of the health system is also usually rapid, establishing prophylaxis measures, or providing vaccination to non-immunized individuals.
Meningitis caused by bacteria such as pneumococcus or meningococcus, is more infrequent than that of viral origin (for example due to enterovirus), but its consequences are worse. In meningitis, the trigger is the arrival into the bloodstream of an infection in another part of the body (the respiratory system generally), until it affects the cerebrospinal fluid and damages the meninges. By the way, more rarely, this disease can occur due to infection caused by fungi, or a traumatic injury to the spine or skull.
Meningitis: infection that requires a rapid response.
As I have commented, contagion is easy when it comes to people who live together part of the day: it is not only about sneezing, coughing, blowing mucus, actions that to a greater or lesser extent disperse the droplets of contaminated secretion; is that these droplets remain on common surfaces such as tables or cutlery, and are transmitted. Let us also bear in mind that there is an incubation period of about four days (which may be greater) during which the affected person could infect others.
I have found this interview with Antonio Salas (Doctor of Medicine and Surgery / Faculty of Medicine of Santiago de Compostela), tells us about a study conducted together with Federico Martinón (head of clinical, infectious and translational pediatrics of a Clinical Hospital. It is a study focused on a genotype of the human genome, analyzing patients with meningococcal disease and healthy individuals. I am particularly struck by the fact that (according to research) 14% of children are genetically protected, thus reducing the chances of developing the disease.
On the other hand, we have also learned by reading the article that this serious infection is associated with morbidity and mortality with 10 percent of deaths, and of the survivors, up to a third do so with serious sequelae. It is very interesting, and it has also helped us to discover that among the symptoms is “fever that is not resolved with antipyretics, bad skin color, coldness in extremities, red-blue pinpoint spots, stiff neck, headache or vomiting” .

How do doctors act?
Early care is essential for better care and resolution of the case, that is why in the event of any suspicious symptoms, do not hesitate to consult; and we will also go to the doctor if someone from our environment has been diagnosed. And by the way, the diagnosis involves extracting fluid with a puncture in the lumbar area: it must be analyzed to find out the origin. If it is bacterial, it will be more serious, but there are also antibiotics to deal with.
A viral meningitis will behave quite safely as other viral infections do: limiting itself, but it is advisable to always receive specialized assistance. Protective measures against damage to other organs, and general medication for symptoms, are within the planned actions.
Meningitis prevention.
In addition to isolating everyone who lives with the patient, we must all know the importance of hand hygiene, which will always protect us from infections. But above all, let's not forget about vaccination: in the vaccination calendar We have financed the vaccine against meningococcus (serotype C), and against serotype B (not financed); in addition to the pneumococcus that is also part of the calendar, of the vaccines whose cost is assumed by the health authority.
Prophylaxis It is also applicable to the companions of the Nursery School and the school, in the event that the patient is a child.
Images - marvin 101, Amanda Mills