In most pregnancies, the placenta is located in the front or back of the uterus.
Placenta previa can occur during pregnancy, but the concept often causes some confusion. Next we are going to delve into aspects around his name.
Placenta
The placenta is an organ essential for the survival and protection of the babyHowever, approaching the end of pregnancy, its function of providing nutrients that move through the maternal bloodstream to the baby diminishes. To the baby It provides you with oxygen and makes it easier to eliminate your stool. Thanks to the placenta, it can subsist inside its mother until the moment of its birth. The placenta is found in the uterus and is made up of a part of the fetus and another of the mother.
As a general rule, when pregnancy begins, the placenta is located in the lower part of the uterus. As the months progress it can move and position itself up. It owes its name from placenta previa, for the reason that when this does not occur, and it does not move, it stays located at the bottom, over the internal cervical os and covers part or all of the neck of the uterus. When the cervix opens during labor, the placenta can separate from the wall.
In most pregnancies, the placenta is in the front or back of the uterus. The one that indicates that it is placed like this specifies its location, but does not give details of any complications. There are mothers who have it on the back or side. Sometimes the placenta previa, which is generally not detected until the ultrasound is performed between the 24th and 26th week of pregnancy, becomes confused with the anterior placenta.
Previous placenta
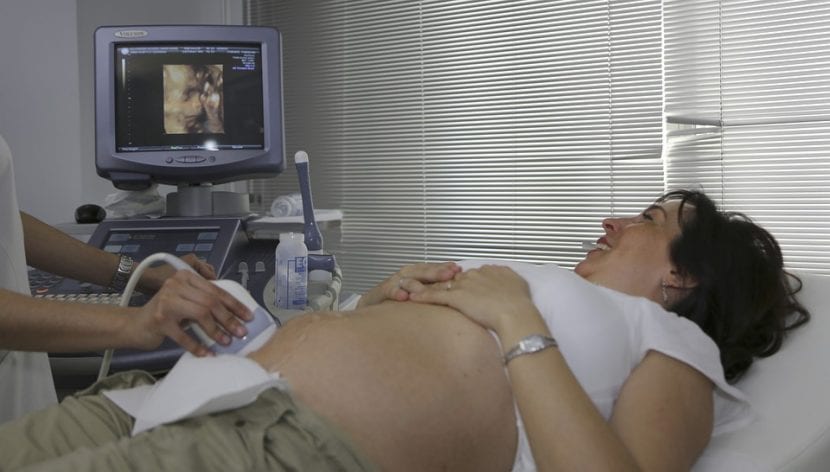
Performing an ultrasound will validate the existence of a placenta previa in the mother.
Having placenta previa is a problem that in principle is not serious for the pregnancy to occur normally and come to fruition. However, should be properly treated so that it does not persist until the third and final trimester, since in this case it could pose difficulties for mother and child. This complication affects 1 in 200 women. Its incidence is higher in women than:
-They are over 35 years of age.
-They have had several pregnancies.
-They have suffered several miscarriages.
-They have a history of surgery on the uterus.
-They have an abnormally shaped uterus.
-They present a habitual consumption of tobacco and cocaine.
-They have a history of placenta previa.
Whether the delivery is vaginal or by cesarean section is determined by the type of placenta previa that exists. These types are as follows:
- Partial occlusive placenta: The placenta covers only part of the cervical os.
- Complete occlusive placenta: The placenta completely covers the opening of the uterus.
- Marginal placenta previa: The placenta reaches the cervix, but without covering it.
- Lateral placenta previa: The placenta is close to the cervix, but does not reach the margins.
How is the placenta previa detected and treated?
The most common thing that happens if with placenta previa, is bleeding, usually of a deep red color. The performance of an ultrasound and subsequent transvaginal ultrasound will validate the existence of a placenta previa in the mother and its position. If the bleeding is abundant, the mother must be admitted and the idea of extracting the baby by cesarean section will be considered. If the bleeding is light, it is normal to schedule the cesarean for week 36. It is not usual for pain to occur, but cramps in the uterus can occur. The diagnosis of placenta previa can also be confirmed, if:
- Contractions occur before normal time.
- The baby comes in a transverse or breech position.
- The size of the uterus is larger than it should be at a certain point in pregnancy.
In addition to bleeding, cesarean section, premature contractions ..., the placenta previa can lead to premature labor. With the placenta previa diagnosed at an early stage, the doctor usually recommends rest to the patient. Rest should be at the pelvic level, that is, the woman should not have vaginal examinations, have intercourse sexuales and limit your travels until the end of pregnancy.
If a mother knows the diagnosis of placenta previa, she can feel overwhelmed and frustrated. exist support groups that you can attend, so that it can be easier for you to cope and get through the trance. The doctor or midwife will also be a key point to guide you during this stage. Other mothers with the same problem can make her not feel alone and know how to handle the situation and expose her fears with them.