
You may have heard of uterine fibroids but may not be quite sure what they really are. Uterine fibroids are muscle tumors that grow on the wall of the uterus or womb. These fibroids are almost always benign, that is, not cancerous. Not all women with uterine fibroids have symptoms, and those that do have symptoms can sometimes be too bothersome.
Other women with uterine fibroids may have heavy menstrual bleeding and pain. The treatment for uterine fibroids will depend on the symptoms that you present as well as the amount or size of them. If you want to know more about uterine fibroids, do not hesitate to continue reading.
Everything you need to know about uterine fibroids
What are uterine fibroids
Fibroids are muscle tumors that are created in the wall of the uterus or womb. Another medical term to refer to them is leiomyoma or simply 'myoma'. They are almost always benign and non-cancerous, it can appear as a single tumor or there can be many of them inside the uterus. Uterine fibroids can be as small as a pear seed or as large as a peach. In some cases they can even be very large and annoying for the woman who suffers from them.
Why You Should Know About Uterine Fibroids
As many as about 20 to 80% of women develop uterine fibroids by the time they reach their 50s. Fibroids are most common in women who are between 40 and 50 years old. Not all women who have fibroids know it because they do not have symptoms, but when they do, it can be very annoying.
Uterine fibroids can also put pressure on the bladder causing the affected woman to have to urinate frequently or even press on the rectum causing constipation or other discomfort. If fibroids become too large, it can cause the abdomen and stomach area to enlarge as if the woman appears to be pregnant, but not pregnant.
Who is at higher risk of uterine fibroids
There are some factors that can increase a woman's risk of suffering uterine fibroids and it is necessary to take them into account in case you feel identified to be able to do the appropriate check-ups:
- Age. Uterine fibroids become more common as a woman ages especially during her 30s to 50s, especially before menopause. When menopause comes, fibroids tend to shrink.
- Genetics. Having a family member with uterine fibroids increases your risk of having them. If a woman's mother had fibroids, then the risk of having them is about three times higher than average.
- Obesity. Women who are overweight are at higher risk of being overweight. For women who weigh more than they should have between two and three times more risk of suffering them.
- Feeding Habits. Eating a lot of red meat or ham is linked to having a higher risk of uterine fibroids. Eating lots of green vegetables can help protect them from reproducing.
What are the symptoms of fibroids
Most uterine fibroids do not cause any symptoms, but some women with fibroids may have the following symptoms:
- Heavy bleeding (which can be heavy enough to cause anemia)
- Painful rules
- Feeling of fullness in the pelvic area (lower stomach area)
- Enlargement of the lower abdomen
- Frequent urination
- Pain during sex or masturbation
- Back pain
- Complications during pregnancy and delivery, including a six times greater risk of undergoing a cesarean section
- Although very rare, it can cause infertility in some cases
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
If you think you may have uterine fibroids, it will be important that you go to your doctor to assess whether you really have and their status. The doctor will do the pertinent tests to make an accurate diagnosis. In addition, it will be your doctor who will assess the type of medications that would be appropriate to take or if it is better to undergo surgery.
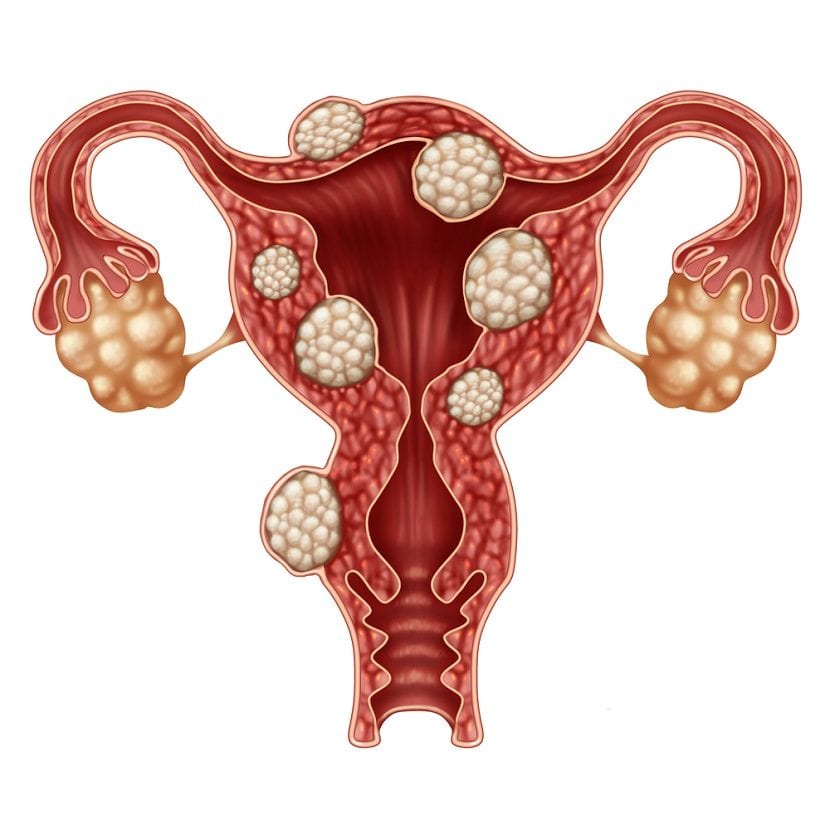
Can a fibroid turn into cancer?
As you may have learned after reading in this article, uterine fibroids are almost always benign and not cancerous. Rarely (1 in 1000 cases) it can turn into a cancerous tumor. This is called a leiomyosarcoma. Doctors believe that these cancers do not arise from the uterine fibroid but that it already exists before. Having uterine fibroids does not increase the risk of developing a cancerous fibroid. What's more, Having them also does not increase a woman's chances of getting other cancers such as uterine cancer.
Pregnancy and uterine fibroids
But what happens if you get pregnant and have uterine fibroids? If you have uterine fibroids you can get pregnant but it is possible that you have more problems both during pregnancy and in childbirth compared to women who do not have them, but this does not mean that they are too serious problems. You can even have a totally normal pregnancy without complications. However, There may be some more common problems in women with uterine fibroids, some of these are:
- Caesarean section. The risk of needing a cesarean section is six times higher for women with uterine fibroids.
- The baby may not be well positioned for a vaginal delivery or that comes from breech.
- Placental abruption (the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before delivery and the baby does not get enough oxygen)
- Premature birth
If you have uterine fibroids and you become pregnant, you should go to your specialist doctor to have good control over your pregnancy. Also, having uterine fibroids doesn't have to be a problem for your everyday life if you don't have painful or other symptoms. On the other hand, if you do have symptoms and they cause you great discomfort, the doctor will look for the best solution to be able to increase your quality of life. Once you have everything under control, you can enjoy your life much more fully and without discomfort of any kind.